Recently, the scientific paper entitled Kinetic Compensation Effect in Logistic Distributed Activation Energy Model for Lignocellulosic Biomass Pyrolysis finished by a team led by Prof. Junmeng Cai from School of Agriculture and Biology at Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU) is published in Bioresource Technology (top journal in the area of Agriculture Engineering). Prof. Junmeng Cai is the corresponding author, Mr. Di Xu from School of Agriculture and Biology at SJTU is the first author, and the co-authors include Ph.D. candidate Meiyun Chai, M.S. candidates Zhujun Dong and Md. Maksudur Rahman from School of Agriculture and Biology at SJTU, and Dr. Xi Yu from European Bioenergy Research Institute of Aston University (UK). The paper can be accessed via ScienceDirect.
Through pyrolysis, lignocellulosic biomass can be converted into liquid fuels (bio-oils) which are easy to store, transport and use. The kinetic study of biomass pyrolysis is fundamental for mechanism investigation, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling and process simulation of biomass pyrolysis. Among various kinetic models, the distributed activation energy model (DAEM) is one of the most comprehensive and accurate models for describing the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass and its components. Compared to the commonly used Gaussian activation energy distribution, the logistic activation energy distribution has slightly thicker tails which makes it better for describing the pyrolysis of biomass components.
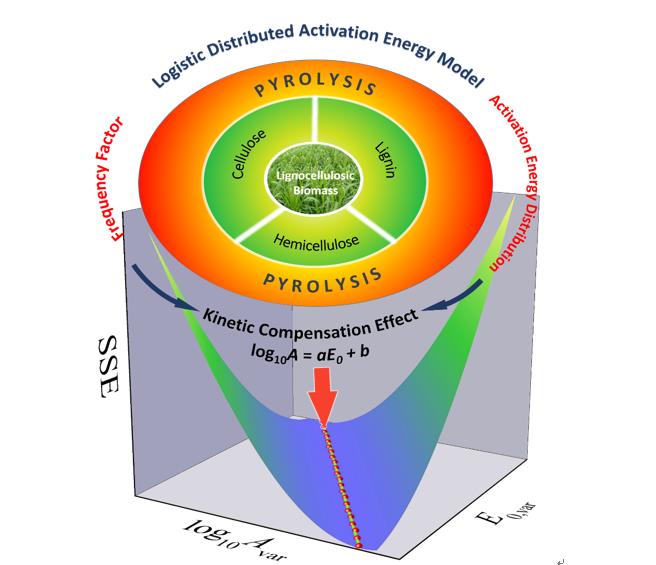
Based on theoretically simulated data and experimental data of the pyrolysis of biomass components, the relationship between the parameters of the logistic DAEM was systematically investigated by means of the sum of square error (SSE) surface tool and the pattern search algorithm. Many parameter sets of the logistic DAEM could fit the data very well for both simulated and experimental data. A perfect linear relationship between the logarithm of the frequency factor and the mean value of the logistic activation energy distribution was found independent on the heating rate. The relationship is called Kinetic Compensation Effect. The results are expected to be helpful for the investigation of biomass pyrolysis mechanism, CFD modeling and process simulation of pyrolysis processes. The methods developed in this research are suitable for analyzing the thermal decomposition kinetics of other solid fuels.