近日,Plant Biotechnology Journal 在线发表新葡的京集团35222vip王文琴研究组题为“The Genetic Architecture of Amylose Biosynthesis in Maize Kernel” 的研究论文。该研究通过全基因组关联分析系统研究了玉米籽粒中表型直链淀粉的含量与单核苷酸多态性的基因型的连锁研究,筛选出了与直链淀粉合成相关的关联SNPs以及有潜力的候选基因,为遗传调控研究玉米淀粉含量和品质改良提供了重要线索。
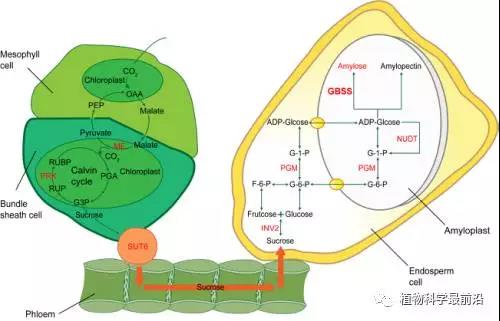
A model of amylose/amylopectin biosynthesis pathway.
淀粉是玉米籽粒中含量最丰富的碳水化合物,主要包含了25%直链和75%左右的支链淀粉。跟总淀粉含量不同的是,直链和支链淀粉的各自所占的百分含量决定了食品原料和工业应用中不同的加工性能。越来越多的研究兴趣转移到遗传控制单个直链或支链淀粉含量上,而它们生物合成的酶反应机器仍不完全清楚。
该团队利用了464株玉米籽粒中表型直链淀粉的含量,以及对应的9,007,194 SNPs的基因型,进行连锁不平衡的全基因组关联分析,筛选出了与直链淀粉合成相关的27个SNPs以及有潜力的39个候选基因,这些结果初步阐明了直链淀粉合成的调控网络,对后续研究和改良玉米籽粒具有重要指导意义。
该研究由新葡的京集团35222vip王文琴与中国科学院上海植物生理生态研究所巫永睿研究组以及沈阳农业大学黄瑞东研究组合作完成,博士生李长生为论文第一作者与博士生黄永才合作完成。相关工作得到了国家科技部七大作物育种和中科院先导项目的资助。该项目所用的自然群体得到中国农业大学赖锦盛教授的大力支持。

Starch is the most abundant storage carbohydrate in maize kernel. The content of amylose and amylopectin confers unique properties in food processing and industrial application. Thus, the resurgent interest has been switched to the study of individual amylose or amylopectin rather than total starch, whereas the enzymatic machinery for amylose synthesis remains elusive.We took advantage of the phenotype of amylose content and the genotype of 9,007,194 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from 454 inbred maize lines. The genome-wide association study (GWAS) identified 27 associated loci involving 39 candidate genes that were linked to amylose content including transcription factors, glycosyltransferases, glycosidases, as well as hydrolases.Except the waxy gene that encodes the granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS), the remaining candidate genes were located in the upstream pathway of amylose synthesis, while the downstream members were already known from prior studies. The linked candidate genes could be transferred to manipulate amylose content and thus add value to maize kernel in the breeding program.